Acupuncture vs. Acupressure: Needle-Free Alternative or Ancient Precision Healing?
Explore the similarities and differences between acupuncture and acupressure, comparing their techniques, benefits, and effectiveness for holistic hea

Audio Summary
Key Takeaways
- Acupuncture and acupressure share roots in Traditional Chinese Medicine
- Both techniques aim to restore balance and promote healing through stimulating acupoints
- Acupuncture uses needles while acupressure applies physical pressure
- Both methods offer benefits for pain management and stress relief
- Choosing between the two depends on individual preferences and specific health needs
The Ancient Healing Arts of Acupuncture and Acupressure
Imagine a world where healing doesn't always involve pills or surgery. This is the realm of acupuncture and acupressure, two ancient practices rooted in Traditional Chinese Medicine. For thousands of years, these techniques have been used to promote health and well-being by tapping into the body's natural energy flow. Both methods focus on stimulating specific points in the body, known as acupoints, to restore balance and alleviate various ailments. While they share common origins, acupuncture, and acupressure differ in their approaches and applications. As more people seek alternative and complementary therapies, understanding these time-honored practices becomes increasingly relevant in our modern quest for holistic health solutions.
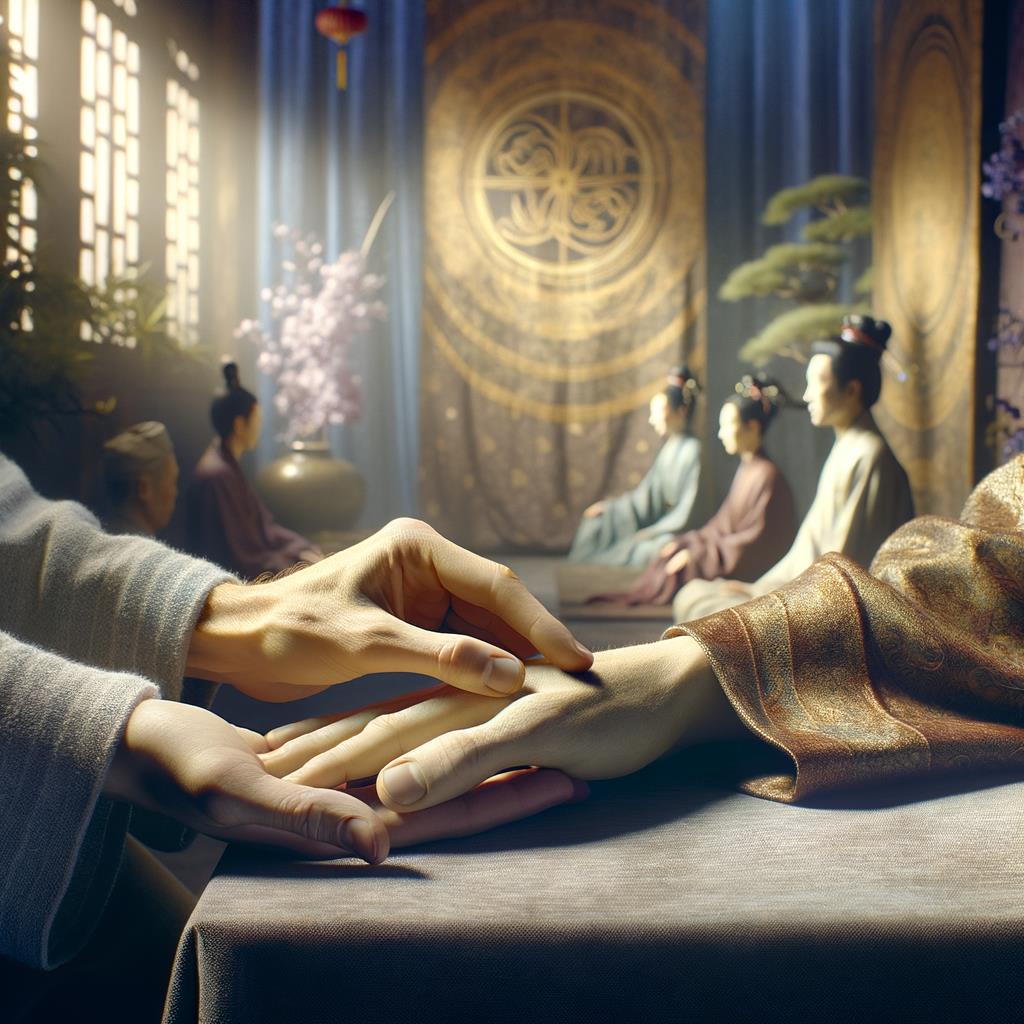

Understanding Acupuncture and Acupressure
Acupuncture and acupressure are ancient healing practices rooted in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM). Both techniques focus on stimulating specific points on the body, known as acupoints, to promote healing and restore balance. These points are believed to lie along energy pathways called meridians, through which vital life force, or 'qi,' flows. In TCM, illness and discomfort are thought to result from blockages or imbalances in this energy flow. By targeting acupoints, practitioners aim to remove these blockages and restore harmony to the body. While acupuncture and acupressure share this fundamental principle, they differ in their application: Acupuncture involves the insertion of thin needles into acupoints and Acupressure applies physical pressure to these same points using fingers, hands, or specialized tools. Both methods are used to address a wide range of physical and emotional concerns, from pain management to stress relief. Understanding these practices provides insight into holistic approaches to health that have endured for millennia and continue to gain recognition in modern wellness circles.
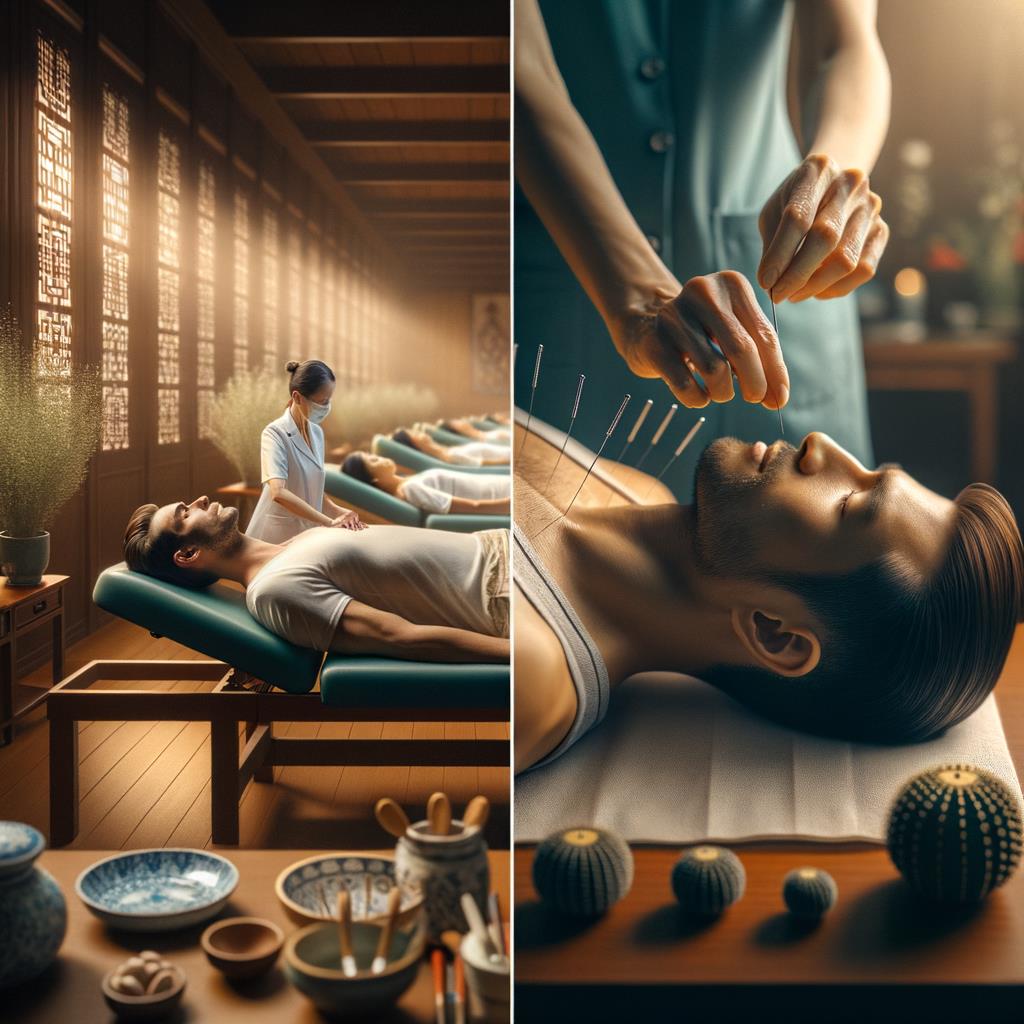

Key Differences Between Acupuncture and Acupressure
While acupuncture and acupressure share common roots, their techniques and applications differ significantly.
Acupuncture:
- Involves inserting thin, sterile needles into specific acupoints
- Needles typically remain in place for 15 to 30 minutes
- Practitioners may gently manipulate needles to enhance therapeutic effect
- Requires specialized training and is usually performed by licensed professionals
- Often conducted in clinical settings
Acupressure:
- Uses firm finger pressure, often applied in a circular motion
- Pressure sustained for several seconds to a few minutes
- Non-invasive nature makes it more accessible for self-treatment
- Easily integrated into daily routines
Sensations: In Acupuncture: Patients often report tingling or mild electrical sensation ('de qi'). In Acupressure: Sensations are generally milder, described as pleasant tenderness or warmth
Applications: In Acupuncture - Suited for complex or chronic conditions (e.g., persistent pain, fertility issues, addiction treatment) and precision and ability to stimulate deeper tissues to address internal imbalances. In Acupressure - Popular for stress reduction, headache relief, and managing nausea, Commonly used as a complementary therapy and Favored by those seeking gentler interventions or with needle phobias.
Understanding these key differences can help individuals make informed decisions about which technique might be more suitable for their specific health needs and personal preferences.
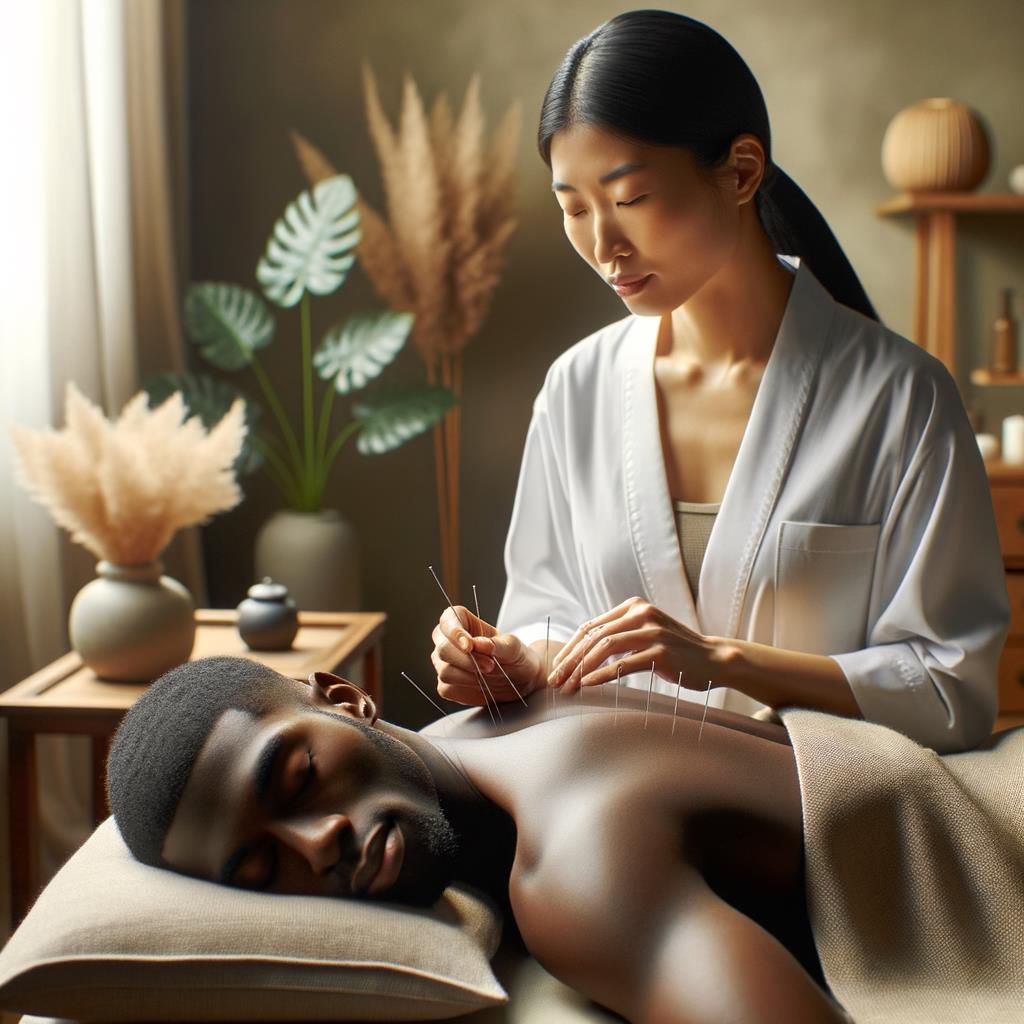

Benefits of Acupuncture and Acupressure for Holistic Healing
Both acupuncture and acupressure offer a range of benefits for holistic healing, supported by a growing body of research.
- Pain Management: Acupuncture: Effective in reducing chronic pain conditions such as lower back pain, osteoarthritis, and migraines. Acupressure: Demonstrated positive results in alleviating various types of pain, including menstrual cramps and postoperative discomfort
- Mental Health: Both techniques have shown promise in managing: Stress, Anxiety, and Depression. Stimulating certain acupoints can trigger the release of endorphins, promoting relaxation and emotional well-being.
- Effectiveness: Acupuncture: Often provides more immediate and pronounced results, particularly for complex health issues. Acupressure: Excellent for ongoing self-care and maintenance of overall wellness
- Additional Benefits: Both techniques have shown potential in: Improving sleep quality, Boosting immune function, and Enhancing overall energy levels. Many patients report improvements in their general sense of well-being and quality of life after treatments.
- Considerations: Individual experiences may vary, effectiveness depends on factors such as practitioner skill, specific condition, and overall health status, and most effective when integrated into a comprehensive health plan including proper nutrition, exercise, and stress management.
While more research is needed to fully understand the mechanisms behind these benefits, acupuncture and acupressure continue to demonstrate their value in holistic healing approaches.
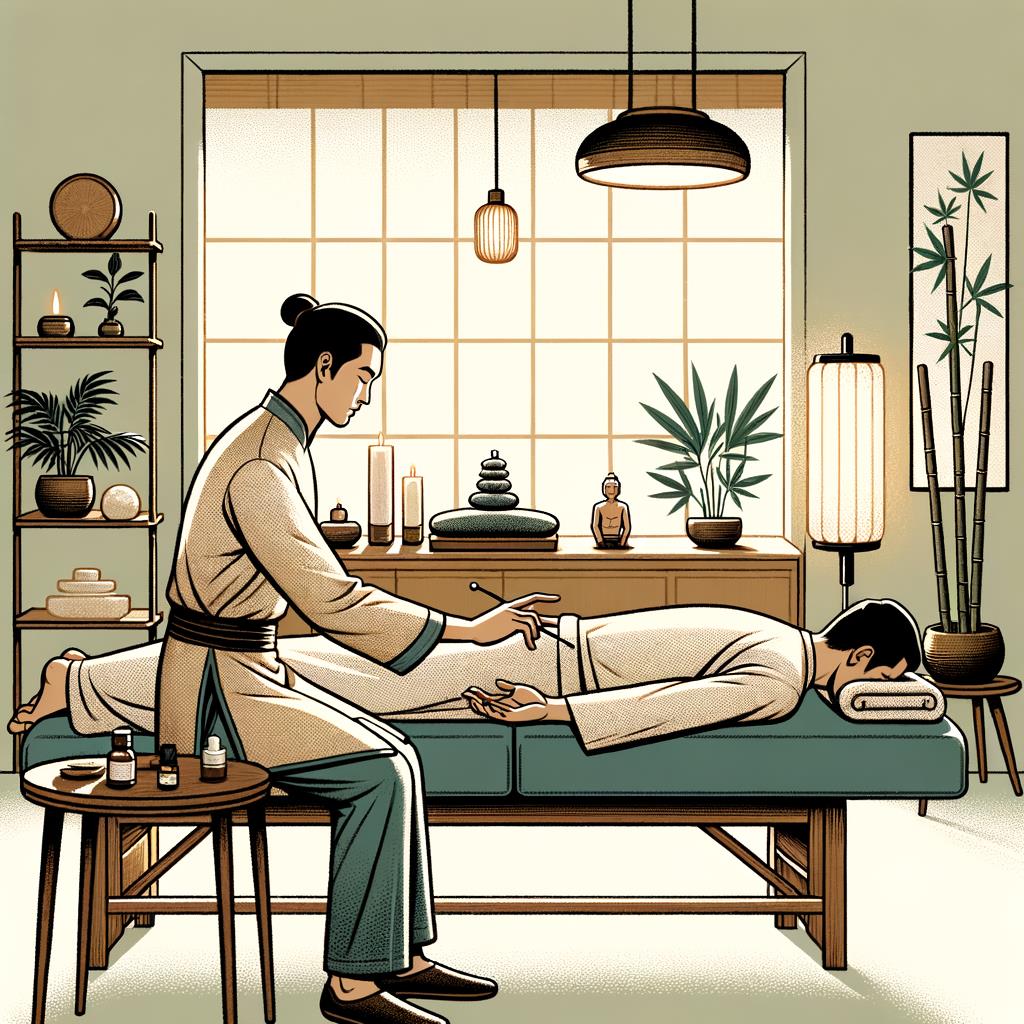

Conclusion: Embracing Acupuncture and Acupressure for Holistic Health
Embracing acupuncture and acupressure for holistic health involves tapping into powerful healing practices rooted in ancient wisdom. While both share origins in Traditional Chinese Medicine, their approaches differ significantly. Acupuncture uses thin needles to stimulate specific body points, offering precise and often intense treatment for various health issues. In contrast, acupressure applies pressure to these same points using fingers or tools, providing a gentler and more accessible option. Both techniques aim to restore balance, promote overall well-being, and improve energy flow throughout the body. They have demonstrated effectiveness in managing pain, reducing stress, and supporting holistic health. Whether you choose the targeted approach of acupuncture or the non-invasive method of acupressure, both offer promising paths to better health and wellness. Consulting with qualified practitioners is essential to determine which approach might best suit your individual needs and preferences. By understanding these time-honored practices, we open ourselves to a world of holistic healing possibilities that complement modern medicine and empower us to take an active role in our health journey.
References
- Acupuncture vs. Acupressure: Similarities & Differences by AIAM (2023). https://www.aiam.edu/acupuncture/acupuncture-vs-acupressure/
- Acupuncture vs Acupressure: Which One to Choose and Why? by Complete Wellness NYC (2024). https://www.completewellnessnyc.com/blog/acupuncture-vs-acupressure
- Acupuncture vs. Acupressure: What's The Difference? by Forbes (2024). https://www.forbes.com/health/wellness/acupuncture-vs-acupressure/
- Where Are Your Pressure Points—And How Can You Use Them? by Health (2023). https://www.health.com/pressure-points-7973884
- Acupressure Points and Massage Treatment by WebMD (2024). https://www.webmd.com/balance/acupressure-points-and-massage-treatment

Related Blog Content

Meditation vs. Mindfulness: Key Differences for Better Mental Health
Explore the key differences between meditation and mindfulness to find out which practice best supports your mental health.
Read More
Herbal Teas vs. Essential Oils: Which Natural Remedy is Best for Stress Relief?
Explore the benefits of herbal teas and essential oils for stress relief, and discover which remedy suits your needs best.
Read More
Discover Aromatherapy: Essential Oils for Holistic Healing and Relaxation
Explore how essential oils can enhance well-being and relaxation through the power of aromatherapy in holistic healing.
Read MoreReady to optimize your biology?
Nutritionaly is free to start. Build better habits, unlock insights, and watch your Bio-Score rise.